Table of Contents
ToggleGnats in house plants might seem like a minor annoyance, but these tiny troublemakers can turn your indoor oasis into a buzzing battleground. If you’ve ever spotted these little pests flitting around your favorite greenery, you know they can be more than just a nuisance. They’re like uninvited guests who refuse to leave the party, and they might even be feasting on your plants’ roots!
Understanding Gnats in House Plants
Gnats can create significant issues within house plants, posing risks to plant health. Recognizing their characteristics and types aids in effective management.
What Are Gnats?
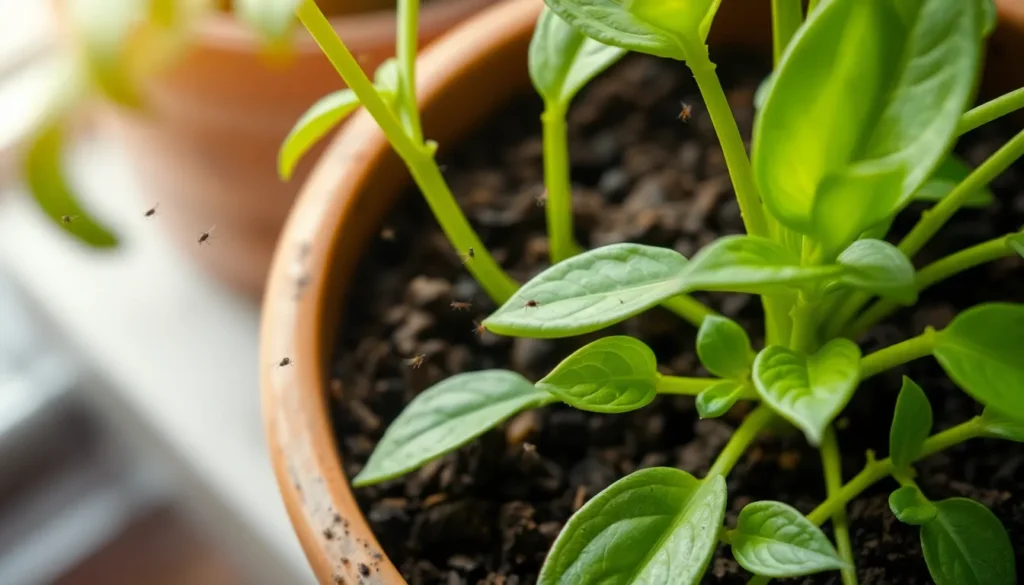
Gnats are small, flying insects belonging to the families Sciaridae and Mycetophilidae. Typically measuring 1/16 to 1/8 of an inch, they appear as tiny black or dark brown flies. Adult gnats often hover around plants, especially near the soil, while larvae dwell in damp, organic-rich soil, feeding on decaying matter and plant roots.
Types of Gnats Commonly Found in House Plants
Several gnat types commonly invade house plants. Fungus gnats thrive in moist, rich soil, often resulting from overwatering. Shore flies, identifiable by their dark bodies, feed on algae and thrive in poorly drained conditions. Additionally, moth flies, resembling tiny moths, occupy damp areas like bathroom plants, where conditions encourage their lifecycle. Maintaining awareness of these types helps prevent infestations.
Causes of Gnats Infesting House Plants

Gnats thrive in house plants primarily due to specific environmental conditions. Identifying these causes helps manage and prevent infestations effectively.
Overwatering and Excess Moisture
Overwatering plants creates an ideal environment for gnats. Soil saturation leads to a moist habitat that attracts fungus gnats. They lay eggs in damp soil, resulting in rapid population growth. Keeping the top layer of soil slightly dry can deter these pests. Monitoring watering habits proves essential for maintaining healthy plants and minimizing gnat activity.
Poor Drainage in Pots
Poor drainage significantly contributes to gnat infestations. Pots without adequate drainage holes trap excess water, fostering a breeding ground for gnats. Moisture accumulates, creating conditions suitable for larvae development. Using well-draining potting mixes helps prevent water logging. Selecting pots designed for effective drainage reduces the likelihood of infestations, protecting plant health.
Signs of Gnat Infestation
Gnats in house plants display several visible signs. Recognizing these signals allows for prompt control measures.
Adult Gnats
Adult gnats measure between 1/16 to 1/8 of an inch. They often hover around plant foliage or near the soil surface. Typical behavior includes flying in erratic patterns, especially around light sources. Observing adults in flight confirms the presence of an infestation. Catching sight of multiple gnats indicates a more serious problem that requires immediate attention.
Larvae in the Soil
Larvae develop in moist soil, thriving in conditions created by overwatering. These tiny, white, worm-like creatures feed on organic matter and plant roots. Noticing a thin layer of larvae in soil or around roots signals a developing infestation. Healthy plants may exhibit stunted growth or yellowing leaves due to root damage caused by larvae. Inspecting the soil regularly helps identify larvae early, thus allowing for effective intervention strategies.
Effective Prevention Methods
Implementing effective prevention methods helps to manage gnats in house plants. Focus on maintaining proper care to create an environment unsuitable for these pests.
Watering Practices
Monitor watering schedules closely to prevent overwatering. Allowing the top layer of soil to dry out between waterings discourages egg-laying by fungus gnats. Consider watering only when plants show signs of dryness. Adjusting humidity levels can also reduce moisture in the soil, further hindering gnat reproduction. Remember that excess moisture creates ideal breeding grounds. Refrain from using trays that collect water underneath the pots. Keeping the soil consistently damp promotes gnat larvae growth.
Choosing the Right Soil
Select potting soil designed for good drainage to reduce gnat infestations. Opt for mixes that include perlite or coarse sand to enhance airflow and moisture management. Such ingredients help avoid water retention while providing essential nutrients. Incorporate organic matter judiciously, as this attracts gnats. Avoid using garden soil, which may harbor pests and reduce overall plant health. Regularly inspect soil for signs of compaction or excessive moisture. Making informed choices about soil types ensures a healthier environment for house plants.
Treatment Options for Infested Plants
Effective treatments for gnats in house plants help restore plant health and combat infestations. Two primary approaches exist: natural remedies and chemical control.
Natural Remedies
Natural remedies offer safe alternatives for managing gnat infestations. Neem oil, for example, disrupts gnat reproduction and promotes healthy plant growth. Diatomaceous earth acts as a physical barrier, causing dehydration in larvae that come in contact with it. Additionally, introducing beneficial nematodes enhances soil health, as these microscopic worms feed on gnat larvae. Keeping the top layer of soil dry for a few days can also break the life cycle of fungus gnats. Regularly mixing in organic materials, like sand, improves drainage while creating unfavorable conditions for breeding.
Chemical Control
Chemical control provides a more immediate solution for severe gnat problems. Insecticidal soap effectively targets adult gnats and larvae alike. When applied as a foliar spray, it disrupts their protective outer layer, leading to dehydration. Pyrethrin sprays also target adult insects and disrupt their nervous systems. Always follow label instructions to ensure safe application. For a systematic approach, consider using granular insecticides designed for soil application. These products release active ingredients over time, targeting gnats in the soil directly. Integrating chemical control methods with preventive practices enhances overall effectiveness against future infestations.
Gnats in house plants can cause significant distress for indoor gardeners. By understanding their behavior and the conditions that foster their presence, it’s possible to take proactive measures. Maintaining proper watering habits and ensuring good drainage are essential steps in preventing infestations. Regular inspections of both soil and plants help catch problems early.
When faced with an infestation, choosing between natural remedies and chemical treatments allows for tailored approaches based on individual preferences. A combination of preventive strategies and effective treatments will ensure a healthier environment for house plants, allowing them to thrive without the intrusion of these pesky pests.